What Is Lawrencium Electron Configuration
Lawrencium is a chemical element with atomic number103 which means there are 103 protons and 103 electrons in the atomic structure. Thechemical symbol for Lawrencium isLr.
Electron configuration ofLawrenciumis[Rn] 5f14 7s2 7p1.
Possible oxidation states are+3.
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of theelectron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thechemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number andarrangement of electrons. Theconfiguration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
It is thePauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom's electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
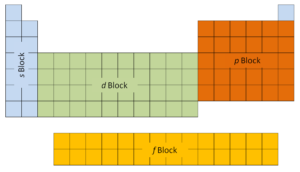 The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled thes block. Similarly, thep blockare the right-most six columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled thes block. Similarly, thep blockare the right-most six columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. The electron configuration can be visualized as the core electrons, equivalent to thenoble gas of the preceding period, and the valence electrons (e.g. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. Most elements have more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4.
"Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…"
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous. An element that is not combined with any other different elements has an oxidation state of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, adding electrons results in a negative oxidation state. We have also distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every element. For example, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4, but only -4, 0 and +4 are common oxidation states.
32
Ge
Germanium
[Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p2
34
Se
Selenium
[Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p4
51
Sb
Antimony
[Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p3
52
Te
Tellurium
[Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p4
73
Ta
Tantalum
[Xe] 4f14 5d3 6s2
74
W
Tungsten
[Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2
78
Pt
Platinum
[Xe] 4f14 5d9 6s1
80
Hg
Mercury
[Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2
104
Rf
Rutherfordium
[Rn] 5f14 6d2 7s2
106
Sg
Seaborgium
[Rn] 5f14 6d4 7s2
109
Mt
Meitnerium
[Rn] 5f14 6d7 7s2
110
Ds
Darmstadtium
[Rn] 5f14 6d8 7s2
111
Rg
Roentgenium
[Rn] 5f14 6d9 7s2
112
Cn
Copernicium
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2
113
Nh
Nihonium
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p1
114
Fl
Flerovium
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p2
115
Mc
Moscovium
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p3
116
Lv
Livermorium
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p4
117
Ts
Tennessine
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p5
118
Og
Oganesson
[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p6
64
Gd
Gadolinium
[Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
71
Lu
Lutetium
[Xe] 4f14 5d1 6s2
91
Pa
Protactinium
[Rn] 5f2 6d1 7s2
93
Np
Neptunium
[Rn] 5f4 6d1 7s2
103
Lr
Lawrencium
[Rn] 5f14 7s2 7p1
What Is Lawrencium Electron Configuration
Source: https://www.periodic-table.org/Lawrencium-configuration-oxidation/

0 Response to "What Is Lawrencium Electron Configuration"
Post a Comment